CSCI 151 - Prelab 5 Straight Up Binary Trees
Due by 10am, Monday 09 October 2017
In this prelab, you will familiarize yourself with some of the design and implementation issues in the upcoming lab 5. Please write or type up your solutions, and hand in a paper copy before class on Monday. Remember, late prelabs receive zero credit.
Part 1 - Binary Trees
As you may recall from class, a binary tree is either:
- empty, or
- a root node of data with a left and right (sub)tree.
Therefore, you will have three classes:
- an abstract class BinaryTree<T> to represent any binary tree,
- a subclass EmptyTree<T> of BinaryTree<T> to represent any empty binary tree, and
- a subclass ConsTree<T> of BinaryTree<T> to represent any non-empty binary tree. ("ConsTree is short for "Constructed Tree".)
private T data;
private BinaryTree<T> left;
private BinaryTree<T> right;
For each of the binary tree methods, you will do the following:
- add it as an abstract method to the BinaryTree class.
- implement the method in the EmptyTree class.
- implement the method in the ConsTree class.
For example, for the height method, you would:
- add the following to BinaryTree:
public abstract int height( ); - add the following to EmptyTree:
public int height( ) { return -1; } - add the following to ConsTree:
public int height( ) { return 1 + Math.max(left.height(),right.height()); }
- Suppose you need a nodeCount method with the following header:
public int nodeCount( )that returns the number of nodes / vertices in the tree (including the root). Write the method body for both the EmptyTree and ConsTree classes. - Suppose you need a leafCount method with the following header:
public int leafCount( )that returns the number of leaves in the tree. Write the method body for this method, presumably using calls to your isLeaf method. Write it for both classes.
- Suppose you need a mirrorImage method with the following header:
public BinaryTree<T> mirrorImage()that returns a new tree that looks like the mirror image of the current tree (that is, a tree "flipped" around a vertical line through the root node). Don't forget to also flip the sub-trees. Write the method body for both classes. - For the following tree, list the nodes as you would encounter them in a post-order, in-order, and pre-order.
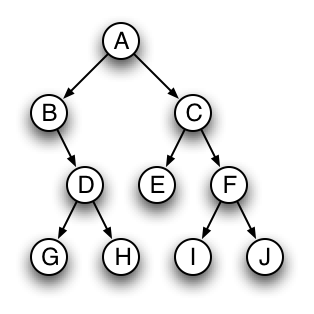
Probably the trickiest method you will write is a method that reads in a binary tree from a file, and returns a new BinaryTree according to the file's contents. It should have the following method signature:
public BinaryTree<String> loadFromFile(String filename)
The files in question will list the nodes of the tree in postorder sequence, one node per line. Each line contains a string, which is the data value stored in the node, and two tag bits. The first tag bit indicates whether or not this node has a left child or not. (1=oui,0=non). The second tag bit indicates whether the node has a right child or not.
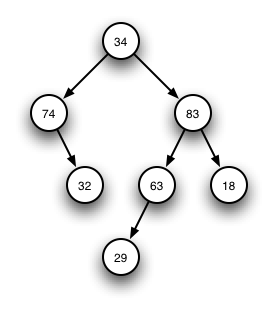 For example, the tree to the right is represented as
For example, the tree to the right is represented as
32 0 0
74 0 1
29 0 0
63 1 0
18 0 0
83 1 1
34 1 1
The information in the file is sufficient to uniquely determine a binary tree. The tree can be constructed from the file using the following pseudocode:
create an empty stack of binary trees (i.e. Stack<BinaryTree<String>>)
while there is another line of input in the file {
read a line (containing data and two tags)
if right tag is 1, pop an element from the stack and call it right
if left tag is 1, pop an element from the stack and call it left
create a new binary tree with data as its root and
left and right as its subtrees (if they exist)
push the new tree onto your stack
}
when you exit the while loop, the stack should contain one element
this element is the the tree represented by the file data (so return it!)
If the stack is empty, the tree has no nodes, so you know what kind of tree it is.
NOTE: the input file is left then right, but the algorithm
uses the right value first, then the left. Not a typo.
- For the following input, run the algorithm above and output the resulting tree (that is, draw the resulting binary tree). Show your stack as you go through the algorithm (you can just draw small trees as the elements on your stack). (You can check that you have the correct tree by running a post-order traversal on it. The nodes in post-order should correspond to the order from the file.)
E 0 0
F 0 0
D 1 1
B 1 0
C 0 0
A 1 1